
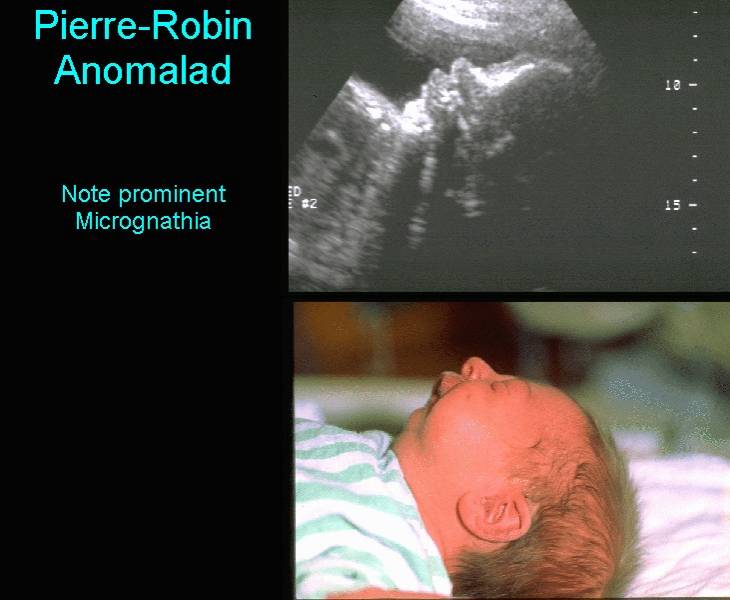
Cases referred for targeted scans included 11 isolated cases of micrognathia or retrognathia, 3 cases of microtia, and 3 cases of auricular or facial vestiges. Visualization of the fetal zygomatic bone was feasible in all low-risk cases. Following this, cases referred for targeted scans for suspected first branchial arch syndrome were assessed for the presence or absence of the zygomatic bones. The feasibility of visualization of the zygomatic bone was performed in 50 sequential fetuses with a normal anatomic scan between 12 and 24 weeks' gestation using 3-dimensional sonography. The aim of this study was to describe the feasibility of visualization of the fetal zygomatic bone and assess its application in cases referred for features suggestive of first arch syndrome.Ī prospective cohort study was conducted. First arch syndrome is classified into 2 main clinical manifestations: Treacher Collins syndrome, characterized by bilateral underdevelopment of the zygomatic bones and Pierre Robin sequence. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.07.First arch syndromes are congenital defects caused by failure of neural crest cells to migrate into the first branchial arch. Prognosis of airway obstruction and feeding difficulty in the Robin sequence. The effectiveness of mandibular distraction in improving airway obstruction in the pediatric population. Tahiri Y, Viezel-Mathieu A, Aldekhayel S, Lee J, Gilardino M. Surgical airway management in Pierre Robin sequence: is there a role for tongue-lip adhesion? Cleft Palate Craniofac J. The surgical correction of Pierre Robin sequence: mandibular distraction osteogenesis versus tongue-lip adhesion. Robin sequences and complexes: causal heterogeneity and pathogenetic/phenotypic variability. Mechanisms of airway obstruction in Robin sequence: implications for treatment. The aetiology and pathogenesis of craniofacial deformity. Etiopathogenesis of isolated Robin sequence. Incidence of the Robin Anomalad (Pierre Robin syndrome). A fall of the base of the tongue considered as a new cause of nasopharyngeal respiratory impairment: Pierre Robin sequence, a translation. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Precise osteotomies for mandibular distraction in infants with Robin sequence using virtual surgical planning. Tip: Most babies outgrow these difficulties by 6 months due to mandibular growth and improved control of the tongue.

The mortality associated with these symptoms is between 1.7 and 11.3% 11. This is performed to rule out other anatomical sites or causes of airway obstruction Prior to any surgical intervention, a nasoendoscopy is recommended. Distraction osteogenesis of the mandible 7,10 is an alternative to tracheostomy.Subperiosteal release of the floor of mouth.Glossopexy: Tongue-lip adhesion for obstruction caused by glossoptosis 9.A nasopharyngeal airway to bypass the obstruction caused by the tongueĪdvance airway management options for Pierre Robin Sequence include 8:.Turn to the newborn prone to relieve the glossoptosis.Generally speaking, syndromic PRS patients are much more challenging to treat than those that occur in isolation. Treatment is focused on the specific needs of each patient, but may include surgery to assist with breathing and feeding modifications to prevent choking. Longer term, patients can often outgrow their clinical issues.
This sequence can be visualised in the illustration below.Īcute management focuses on airway and feeding management. Defect 3: U-shaped cleft palate due to blocked closure of the palatal shelvesĪ small jaw results in the tongue occupying more significanter proportion of the oropharynx and falling back to cause airway obstruction.Defect 2: Glossoptosis due to posterior displacement of the tongue.Defect 1: Micrognathia due to mandibular hypoplasia.It is called a "sequence" because a single developmental defect results in a chain of secondary defects. It can be syndromic or occur in isolation. Pierre Robin Sequence is a congenital group of defects resulting in upper airway obstruction and failure to thrive. Long-term patients will often outgrow issues with airway and feeding. Rare and linked to Stickler, Nagar and Treacher Collins SyndromeĪcute management for airway and feeding. Micrognathia, Glossoptosis and U-shaped Palate result in upper airway obstruction and failure to thrive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
